

An IP address is written in "dotted decimal" notation, which is 4 sets of numbers separated by period each set representing 8-bit number ranging from (0-255).

Due to IPv4 addresses running out, a new version of the IP protocol (IPv6) has been invented to offer virtually limitless number of unique addresses. The traditional IP Addresses (IPv4) uses a 32-bit number to represent an IP address, and it defines both network and host address. An IP address is analogous to a street address or telephone number in that it is used to uniquely identify a network device to deliver mail message, or call ("view") a website.
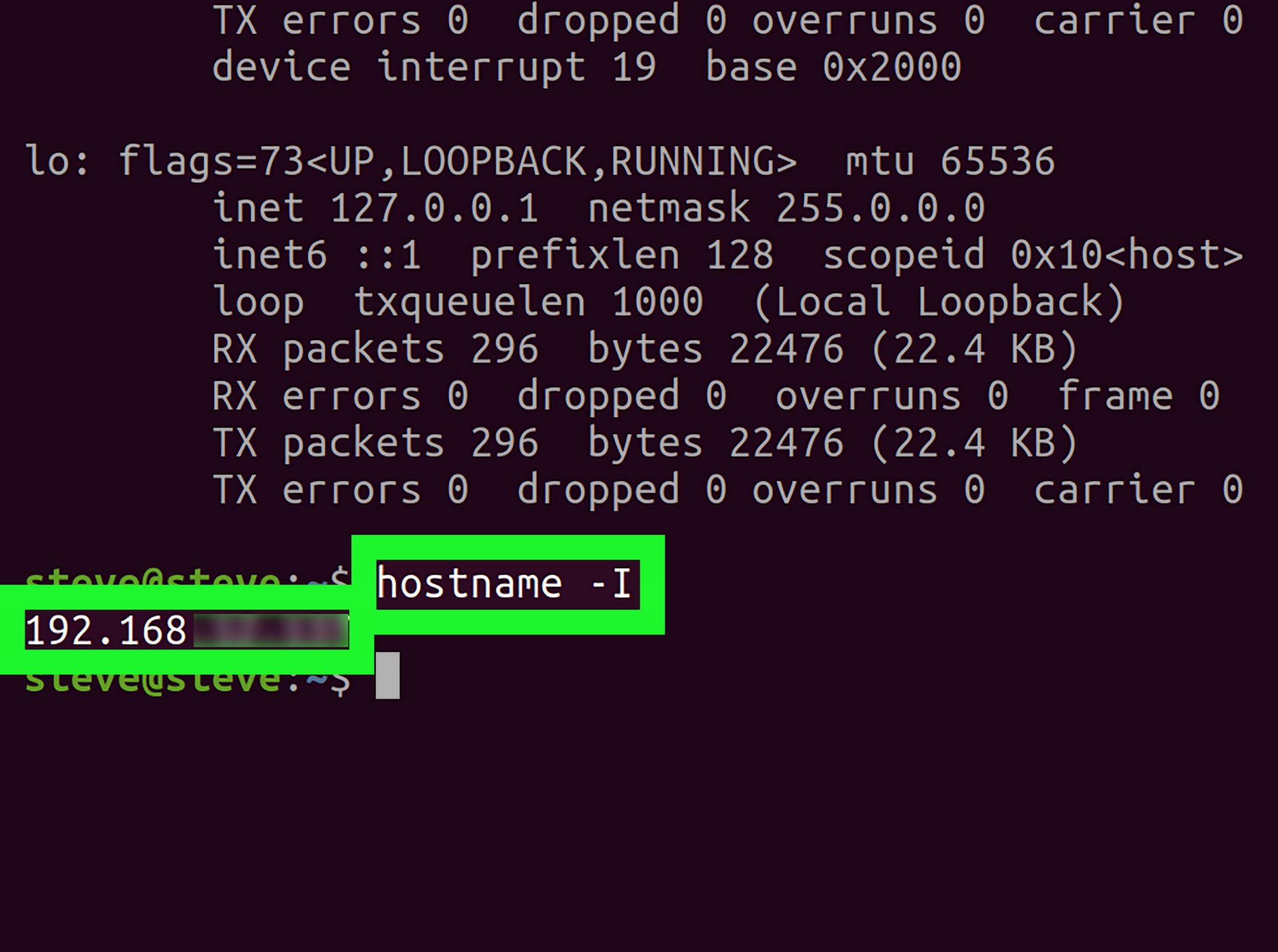
Any device connected to the IP network must have an unique IP address within its network. Internet Protocol Address (or IP Address) is an unique address that computing devices use to identify itself and communicate with other devices in the Internet Protocol network.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
